BMW 3: Removing the round high-voltage connector
The following figures show the approach for releasing the round high-voltage connector, as used for example on the high-voltage cable from the Electrical Machine Electronics to the convenience charging electronics.
Depending on the installation location, different connectors may be used. They are distinguished by an additional black sliding piece at the connector. The following graphic shows both variants.
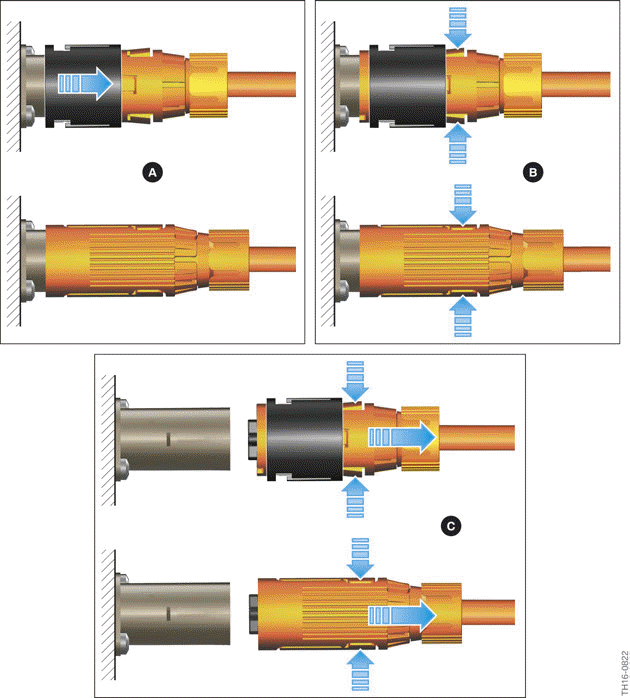
Removing the round high-voltage connector
- The round high-voltage connector is connected to the high-voltage
connection of the corresponding high-voltage component and locked.
In the case of connectors with a black sliding piece, the sliding piece must be pushed to the end position in the direction of arrow. - The two locking elements must be pressed together in the direction of arrow. The mechanical lock of the connector at the connection of the high-voltage component is then removed.
- While the locking elements are being pushed closed together, the connector must be removed in direction of arrow.
When reconnecting the high-voltage cable the locking elements must not be pushed together.
Instead, it is sufficient to slide the connector onto the high-voltage connection of the component and push the sliding piece towards the high-voltage component if needed. Ensure that the locking elements engage ("clicking" noise). In addition, the engaging of the locking elements should be checked by subsequent pulling on the connector.
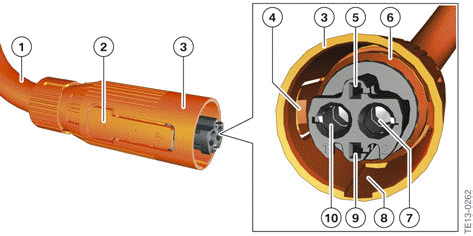
Example of structure of the round high-voltage connector
- High-voltage cable
- Actuation points on locking elements
- Connector housing
- Locking element
- Connection 1 for bridge in the connector
- Connection for shielding
- High-voltage connection, pin 2
- Mechanical encoding
- Connection 2 for bridge in the connector
- High-voltage connection, pin 1
In contrast to earlier high-voltage connectors, the connections for the bridge in the high-voltage connector are not evaluated in the G20 PHEV.

